In a new
essay, Vitalik Buterin, highlights how Ethereum's validator set
size could be a threat to network decentralization and performance.
This may come as a surprise as it’s generally understood that a
larger validator set means less centralization and a stronger
network, however it’s not quite that simple. Outlined below are
reasons why the growing validator set size poses challenges for the
Ethereum network:
-
Strain on Network Infrastructure: A large
validator set size places significant strain on the peer-to-peer
networking and messaging infrastructure of the Ethereum network.
With more validators, there are higher computational loads and
bandwidth requirements, which can lead to node failures and
reduced network reliability. This can make it challenging for the
Ethereum network to maintain robust peer-to-peer communication,
potentially leading to increased centralization as only
well-equipped nodes can participate effectively.
-
Technical Debt: A growing validator set size
creates technical debt that can complicate the implementation of
future upgrades and improvements to the Ethereum network. It can
make upgrades, such as achieving single slot finality (SSF),
riskier and more complex. Technical debt can slow down the
development and implementation of important features, potentially
hindering the network's ability to evolve and adapt.
-
Resource Requirements: As the validator set size
grows, validator node operators are required to invest in more
powerful hardware and network infrastructure to support the
increasing bandwidth and message propagation demands. This can
favor larger, more centralized entities capable of affording such
resources, potentially discouraging smaller, independent node
operators.
-
Complexity of Upgrades: Ethereum's PoS
consensus mechanism relies on a combination of models, including
LMD GHOST and Casper FFG, to balance chain liveness and finality.
Managing these models becomes increasingly complex as the
validator set size grows, making upgrades and changes more
challenging to implement effectively.
To address these concerns and maintain decentralization, Ethereum
developers are considering various solutions, both short-term and
long-term:
-
Short-Term Solutions: Developers have proposed
short-term solutions like capping the validator entry churn to
limit the growth of the validator set size. While this can provide
immediate relief, it may have second-order effects, such as
discouraging new validators from joining and concentrating rewards
among existing validators.
-
Increasing Validator Maximum Effective Balance:
One long-term solution being considered is increasing the maximum
effective balance that validators can hold. This would allow
validators to earn more rewards without requiring them to create
multiple smaller validators. However, this proposal also presents
complexities and potential centralization risks.
-
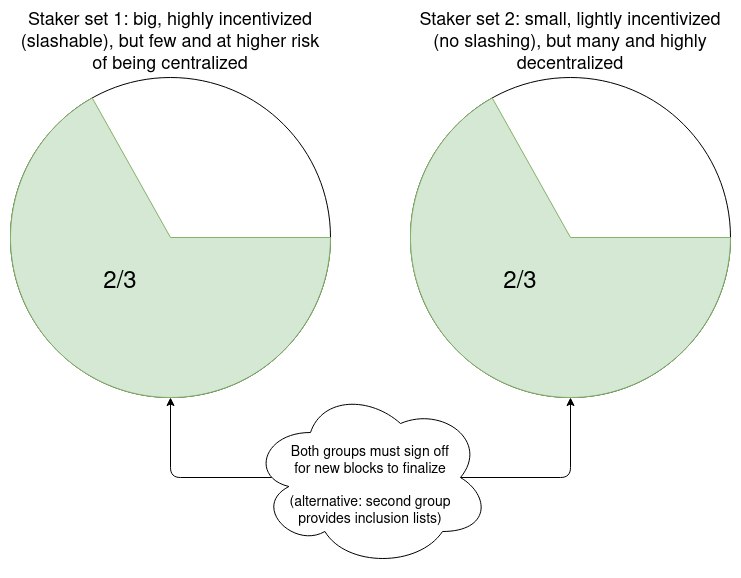
Super-Committees, Economic Capping, and Floating Minimum
Balance: Other long-term solutions under discussion include the use of
super-committees, economic capping of total deposits, and a
floating minimum balance. These approaches aim to limit the
validator set size over time while considering the potential
impact on network security and decentralization.
In conclusion, the growth of Ethereum's validator set size
poses challenges related to network performance, technical
complexity, and centralization risks. To mitigate these threats,
Ethereum developers are exploring various strategies, but finding
the right balance between decentralization and network scalability
remains a complex and evolving challenge in the ongoing development
of the Ethereum network.
Stay Connected!
Don't miss out on anything as we embark on this incredible
adventure. Follow us on all our social media channels, join us on
this journey, and be a proud Web3 Evangelist!
Join us today and be a part of the Web3 revolution!
W3E
Telegram groups